Unveiling the Secrets of Ghosted Domains
Explore the intriguing world of expired domains and online opportunities.
A Web Without Barriers: Everyone's Invitation to the Internet
Unlock the web for all! Discover how to create an inclusive internet experience that invites everyone to join the digital revolution.
Understanding Accessibility: Why a Barrier-Free Web is Essential for Everyone
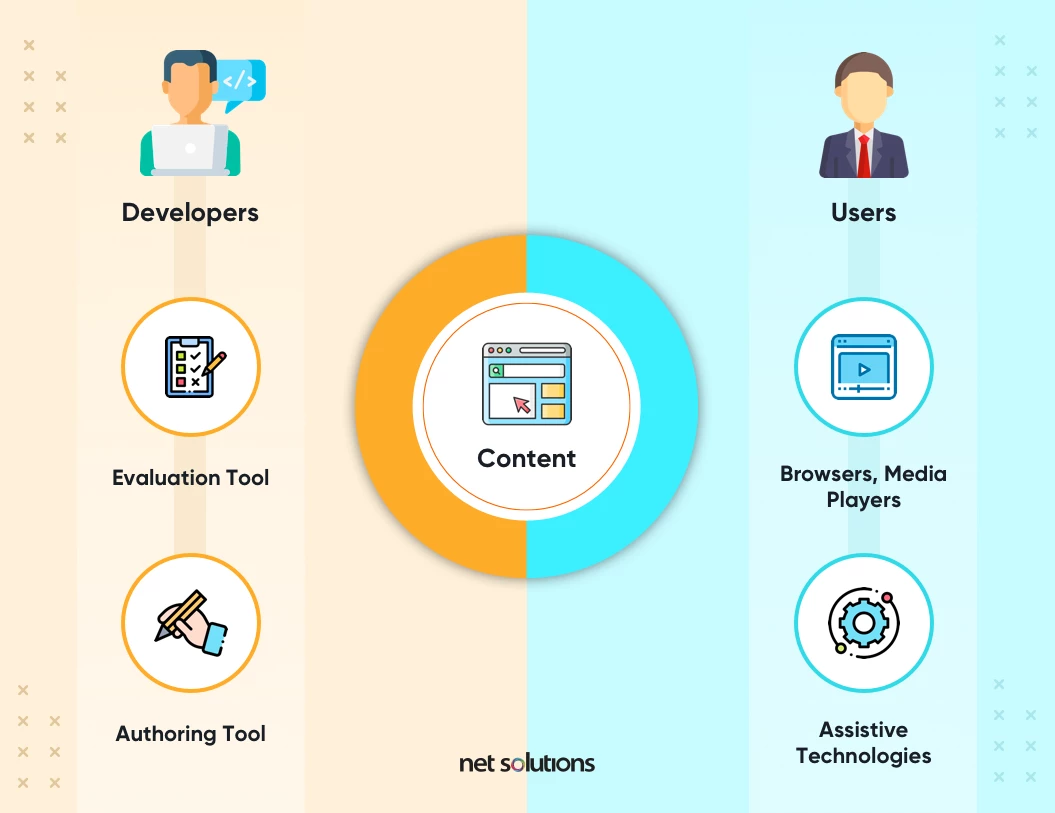
Understanding accessibility is crucial in today's digital landscape, as it ensures that all individuals, regardless of their abilities, can access and interact with online content. A barrier-free web allows people with disabilities—such as visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments—to navigate the internet effectively. Moreover, creating an inclusive digital space not only benefits those with disabilities but also enhances the user experience for everyone. An accessible website can lead to better engagement, lower bounce rates, and increased customer satisfaction, making it a win-win for businesses and users alike.
Implementing accessibility features involves a range of practices and guidelines, such as improving keyboard navigation, ensuring adequate color contrast, and providing text alternatives for non-text content like images and videos. By embracing these principles, we can create a more equitable online environment. Ultimately, understanding accessibility means recognizing that a barrier-free web is essential for fostering inclusivity, promoting diversity, and ensuring that no one is left behind in the digital age.
Top 10 Web Accessibility Practices to Ensure Inclusivity
Ensuring web accessibility is crucial for creating an inclusive online environment. By implementing the top 10 web accessibility practices, website owners can make their content accessible to individuals with disabilities, which in turn enhances user experience for all. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Use Semantic HTML: Properly using HTML elements like headings, lists, and links helps to convey meaning and structure to screen readers.
- Provide Text Alternatives: Utilize
altattributes for images and other non-text content to ensure that all users can understand the material. - Ensure Keyboard Accessibility: All interactive elements should be navigable via keyboard alone, making it easier for users with mobility issues.
- Utilize ARIA Roles: Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) roles can enhance the usability of complex components, ensuring they are comprehensible to assistive technologies.
- Maintain Color Contrast: Sufficient color contrast between text and background enhances readability for visually impaired users.
Continuing with the top web accessibility practices, it's essential to prioritize usability for all users:
- Ensure Consistency: Keep navigation consistent throughout the site to minimize confusion and aid in easier navigation.
- Implement Responsive Design: A responsive layout can enhance accessibility across various devices, including desktops, tablets, and mobile phones.
- Avoid Automatic Media Playback: Users should have control over audio and video content to prevent disorientation and ensure a comfortable browsing experience.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Any form fields or interactive elements should have clear labels and instructions to guide all users effectively.
- Test for Accessibility: Regularly conduct accessibility audits and usability testing with real users to identify areas for improvement.
What Does an Accessible Website Look Like? Key Features Explained
An accessible website is designed to be usable by all individuals, including those with disabilities. To achieve this, several key features must be incorporated. First, a well-structured layout using semantic HTML ensures that assistive technologies, like screen readers, can effectively interpret the website's content. For instance, using <header>, <nav>, <main>, and <footer> tags organizes the page for better navigation. Additionally, implementing alt text for images allows visually impaired users to understand visual content through descriptions, making the site more inclusive.
Another crucial aspect of an accessible website is the use of color contrast and text size that accommodates various readability needs. Websites should ensure that text stands out against the background, adhering to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). Implementing keyboard navigation is also essential, as many users rely on keyboard shortcuts. This practice allows users to navigate through content efficiently without needing a mouse. In essence, an accessible website isn't just about meeting legal requirements; it enriches the experience for all users, promoting inclusivity and engagement.